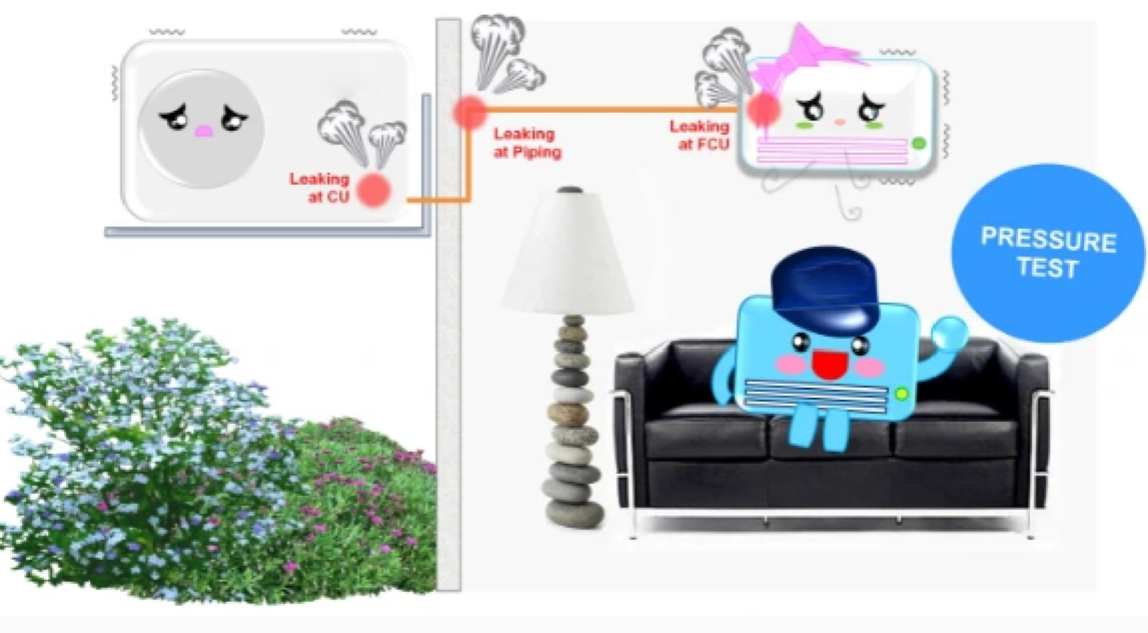
REPAIR
Experiencing weak cooling, unusual noises, or system breakdowns? Our skilled technicians are ready to diagnose and repair all types of air conditioning issues quickly and efficiently. We handle everything from minor faults to major component replacements, restoring your comfort with minimal downtime. With prompt service and quality workmanship, we ensure your system runs smoothly again in no time.
.png)